Unit 1
Introduction to Data Communication Definition: Effectiveness, Basic Communication Components. Network Architecture Definition, History, Criteria, Goals and Applications of Networks, Categories of networks, Organization of the Internet, ISP, Protocols and standards, The OSI reference model, TCP/IP protocol suite, Network devices and components. Network topology design, Types of connections.
Q221 – A devices that links two homogeneous packet-broadcast local networks, is
hub
bridge
repeater
gateway
Ans – (2)
Explanation –
Bridge connects two similar or homogeneous networks (such as two Ethernet networks) and operates at the Data Link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model. It can filter and forward data between these networks based on MAC addresses.
Q222 – Which of the following device copies electrical signals from one Ethernet to another?
hub
bridge
repeater
passive hub
Ans – (3)
Explanation –
A repeater is a device that regenerates or amplifies electrical signals before sending them to the next segment of a network. It operates at the physical layer (Layer 1) of the OSI model and is used to extend the distance of a network by refreshing the signal. It essentially copies electrical signals from one Ethernet segment to another to maintain signal integrity over longer distances.
Q223 – If communication software can be called the “traffic cop” of a micro communication system, then what should the modem be called?
Link
Park
Bridge
Interface
Ans – (3)
Explanation – A bridge connects two similar or homogeneous networks, allowing them to communicate with each other. It operates at the Data Link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model, managing data flow based on MAC addresses. Similarly, a modem facilitates communication between different types of networks or systems, bridging the gap between them.
Q224 – Repeaters are often used on an 802.3 network to help strengthen the signals being transmitted. As with the length of segments and the number of segments, a limit exists as to how many repeaters can be used between any two nodes. What is the maximum number of repeaters that can be used?
1
4
9
12
Ans – (2)
Explanation –
This limitation is defined to ensure that the signal quality remains within acceptable limits and that the network operates reliably.
Each repeater extends the network segment by regenerating the signal, but after a certain number of repeaters, the signal degradation can affect network performance and reliability. Therefore, the Ethernet standard typically limits the number of repeaters to 4 between any two nodes.
Q225 – Consider the below figure. What are the bits transmitted for the Unipolar system?
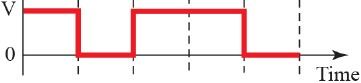
01101
11010
10110
01001
Ans – (3)
Q226 – Ethernet uses a ______ physical address that is imprinted on the network interface card (NIC).
32-bit
64-bit
6-byte
none of the above
Ans – (3)
Explanation –
Ethernet uses a 6-byte (48-bit) physical address known as the MAC (Media Access Control) address. This address is unique to each network interface card (NIC) and is assigned by the manufacturer. The MAC address is essential for network communication, as it helps devices on the same network to identify and communicate with each other.
The MAC address is typically displayed in hexadecimal format, divided into six pairs separated by colons or hyphens (e.g., 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E). This unique identifier helps ensure that data packets are delivered to the correct device within a local network.
Q227 – You have 10 users plugged into a hub running 10Mbps half-duplex. There is a server connected to the switch running 10Mbps half-duplex as well. How much bandwidth does each host have to the server?
100 kbps
10 Mbps
1 Mbps
2 Mbps
Ans – (2)
Explanation –
In this scenario, we have a hub with 10 users connected, and a server connected to a switch. Both the hub and the server are running at 10Mbps half-duplex. It’s important to understand how bandwidth works in a half-duplex network using a hub.
A hub shares the total available bandwidth among all connected devices. Since it is a half-duplex connection, data can only be sent or received at one time, not simultaneously.
- Each user shares the 10 Mbps bandwidth provided by the hub.
- If only one device communicates with the server at a time, it can use the full 10 Mbps.
- If multiple devices communicate simultaneously, they share the 10 Mbps bandwidth.
Despite potential sharing, each host theoretically has the potential to use up to the full 10 Mbps to the server if they are the only ones communicating at that time.
Q228 – How different computers are connected to a LAN by a cable?
Interface card
Modem
DSL
DSLAM
Ans – (1)
Explanation –
Computers are connected to a Local Area Network (LAN) using an interface card, also known as a Network Interface Card (NIC). The NIC allows computers to connect to the network via Ethernet cables.
An interface card (NIC) is installed in each computer and connects to the LAN using a cable.
Q229 – On an Ethernet network, this is the unit of data that is transmitted between network points. It has explicit minimum and maximum lengths and a set of required pieces of information that must appear within it.
data-chunk
frame
data packet
packet
Ans – (2)
Explanation –
On an Ethernet network, the unit of data that is transmitted between network points, with explicit minimum and maximum lengths and required pieces of information, is called a frame.
An Ethernet frame is the fundamental unit of data transmission on an Ethernet network. It includes headers and trailers with required information such as source and destination MAC addresses, as well as the actual data payload.
Q230 – This is a device that can be used to connect one Ethernet network to another nearby Ethernet network.
gateway
switch
bridge
forwarder
Ans – (3)
Explanation – The device that can be used to connect one Ethernet network to another nearby Ethernet network is called a bridge.
A bridge connects two separate Ethernet networks together to form a larger network. It operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model and uses MAC addresses to filter and forward data between the two networks.
Q231 – What is the hexadecimal equivalent of the Ethernet address 01011010 00010001 01010101 00011000 10101010 00001111?
5A:88:AA:18:55:F0
5A:81:BA:81:AA:0F
5A:18:5A:18:55:0F
5A:11:55:18:AA:0F
Ans – (4)
Explanation –
Binary: 01011010 00010001 01010101 00011000 10101010 00001111
Convert each group of 8 bits (1 byte) into hexadecimal
01011010 = 5A
00010001 = 11
01010101 = 55
00011000 = 18
10101010 = AA
00001111 = 0F
Combine all hexadecimal pairs with colons to separate them
5A:11:55:18:AA:0F
Q232 – If an Ethernet destination address is 07:01:02:03:04:05, then this is a ______ address.
unicast
multicast
broadcast
any of the above
Ans – (2)
Explanation –
A multicast address is used to send data packets to a specific group of devices on the network. Devices that are interested in receiving packets sent to a multicast address join the multicast group associated with that address.
In the case of the Ethernet destination address 07:01:02:03:04:05, since the least significant bit of the first byte (07 in hexadecimal) is set to 1, this indicates that it is a multicast address. Multicast addresses allow efficient distribution of data to multiple devices interested in the same information, such as in streaming applications or certain network protocols.
07 – 0000 0111
The least significant bit of first octant 0 then unicast.
The least significant bit of first octant 1 then Multicast.
entire 8 bits are 1’s of first octant then broadcast.
Q233 – If an Ethernet destination address is 08:07:06:05:44:33, then this is a ______ address.
unicast
multicast
broadcast
any of the above
Ans – (1)
Explanation –
A unicast address is used to send data packets to a specific single device on the network. Unicast addresses are identified by having the least significant bit of the first byte (most significant byte) set to 0.
08 – 0000 1000
The least significant bit of first octant 0 then unicast.
The least significant bit of first octant 1 then Multicast.
entire 8 bits are 1’s of first octant then broadcast.
Q234 – Which of the following could not be an Ethernet unicast destination?
43:7B:6C:DE:10:00
44:AA:C1:23:45:32
46:56:21:1A:DE:F4
48:32:21:21:4D:34
Ans – (1)
Explanation –
To determine which of the following Ethernet addresses could not be a unicast destination, we need to check the format of each address. A unicast Ethernet address has the least significant bit of the first byte (most significant byte) set to 0.
43 – 01000011
Least significant bit is 1, so this is not a unicast address.
Q235 – Which of the following could not be an Ethernet multicast destination?
B7:7B:6C:DE:10:00
7B:AA:C1:23:45:32
7C:56:21:1A:DE:F4
83:32:21:21:4D:34
Ans – (3)
Explanation – To determine which of the following Ethernet addresses could not be a multicast destination, we need to check the format of each address. A multicast Ethernet address has the least significant bit of the first byte (most significant byte) set to 1.
7C – 01111100
Least significant bit is 0, so this could not be a multicast address.
Q236 – In Ethernet addressing, if all the bits are 1s, the address is _________.
unicast
multicast
broadcast
none of the above
Ans – (3)
Explanation –
The least significant bit of first octant 0 then unicast.
The least significant bit of first octant 1 then Multicast.
entire 8 bits are 1’s of first octant then broadcast.
Q237 – ______defines a protocol data unit (PDU) that is somewhat similar to that of HDLC.
MAC
LLC
LLU
none of the above
Ans – (2)
Explanation –
The protocol data unit (PDU) that is somewhat similar to HDLC (High-Level Data Link Control) is defined by LLC (Logical Link Control).
The LLC sublayer provides error control, flow control, and framing of packets. It interfaces with the upper layers (such as network layer protocols like IP) and handles multiplexing of protocols over the same medium.
Q238 – In the Ethernet, the _______field is actually added at the physical layer and is not (formally) part of the frame.
CRC
preamble
address
none of the above
Ans – (2)
Explanation – In Ethernet, the preamble field is actually added at the physical layer and is not formally considered part of the frame.
The preamble is a sequence of bits (typically 8 bytes) added at the beginning of the Ethernet frame. It is used for synchronization and helps the receiving devices synchronize their clocks with the incoming data.
The preamble is added at the physical layer (Layer 1) of the OSI model. It precedes the actual Ethernet frame and is not formally considered part of the frame structure in terms of higher-layer protocols and processing.
Q239 – The protocol used in ETHERNET?
ALOHA
Binary Count down
CSMA/CD
Multiple Access Protocol
Ans – (3)
Explanation –
CSMA/CD is the Ethernet protocol used for managing access to the network medium, where devices listen (Carrier Sense) to determine if the network is idle before transmitting, and in the event of a collision (Collision Detection), devices follow a backoff algorithm to retransmit data.
Q240 – In Token Ring, Which of the following is not a transceiver function ?
Transmission and receipt of data
Checking of line voltages
Addition and subtraction of header
Collision
Ans – (3)
Explanation –
In Token Ring networks, the function that is not typically performed by a transceiver is Addition and subtraction of header.
Transceivers in Token Ring networks primarily handle the transmission and reception of data, as well as checking line voltages to ensure proper signalling and connectivity. The addition and subtraction of headers are typically handled by higher-level protocols or network interface controllers (NICs), rather than by the transceiver itself.



