Unit 1
Introduction to Data Communication Definition: Effectiveness, Basic Communication Components. Network Architecture Definition, History, Criteria, Goals and Applications of Networks, Categories of networks, Organization of the Internet, ISP, Protocols and standards, The OSI reference model, TCP/IP protocol suite, Network devices and components. Network topology design, Types of connections.
Q181 – In an optical fiber, the inner core is _______ the cladding.
denser than
less dense than
the same density as
another name for
Ans – (1)
Explanation –
Optical Fiber Structure – An optical fibre consists of a core, which is the innermost part where light travels, surrounded by a cladding layer. The core has a higher refractive index compared to the cladding, which means it is denser optically. This difference in refractive index allows light to be guided down the fibre through total internal reflection.
Function of Core and Cladding – The core’s higher refractive index ensures that light traveling through it is confined and guided within the core, minimizing signal loss and maintaining signal integrity. The cladding, with a lower refractive index, serves to surround the core and help contain the light within the core by reflecting it back into the core when it tries to escape.
Q182 – The inner core of an optical fiber is _______ in composition.
Glass or plastic
Copper
Bimetallic
Liquid
Ans – (1)
Explanation –
Optical fibers are made primarily of glass or sometimes plastic materials for the core, surrounded by another layer of glass or plastic for the cladding. This composition allows for efficient transmission of light through the fiber, as glass and certain plastics have suitable optical properties (refractive index) to guide light via total internal reflection.
Glass or Plastic Core – These materials are chosen for their transparency to light and their ability to maintain the integrity of the optical signal over long distances.
Q183 – When a beam of light travels through media of two different densities, if the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, _______ occurs.
Reflection
Refraction
Incidence
Criticism
Ans – (1)
Explanation – When a beam of light travels through media of two different densities, if the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, reflection occurs.
The critical angle is the angle of incidence at which light traveling from a denser medium to a less dense medium is refracted at an angle of 90 degrees with respect to the normal. If the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle, total internal reflection occurs instead of refraction.
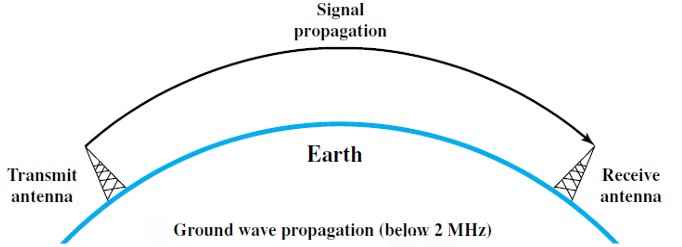
Q184 – Signals with a frequency below 2 MHz use _______ propagation.
Ground
Sky
Line-of-sight
None of the above
Ans – (1)
Explanation –
Ground Propagation – Also known as ground wave propagation, it refers to the method by which radio signals with frequencies below approximately 2 MHz travel along the surface of the Earth, following its curvature.
This type of propagation allows for long-distance communication, particularly useful for AM radio broadcasting and certain types of shortwave communications.
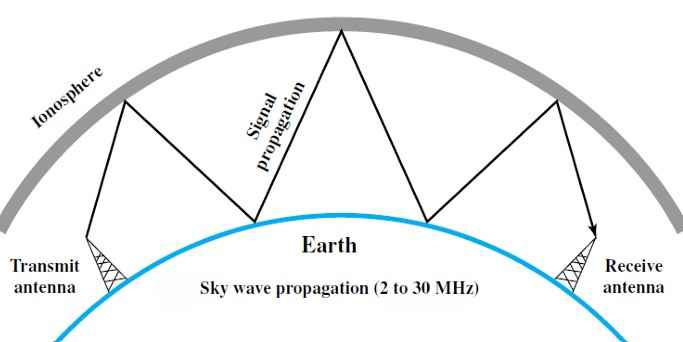
Q185 – Signals with a frequency between 2 MHz and 30 MHz use ______ propagation.
Ground
Sky
Line-of-sight
None of the above
Ans – (2)
Explanation –
Sky Propagation – Frequencies between 2 MHz and 30 MHz are in the High Frequency (HF) range. In this range, radio waves are refracted by the ionosphere, allowing them to travel long distances by bouncing between the ionosphere and the Earth’s surface. This type of propagation is known as sky wave propagation and is essential for long-distance communication, especially over the horizon.
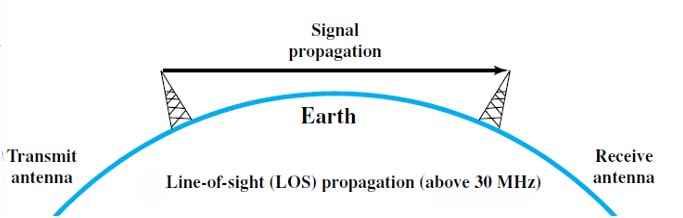
Q186 – Signals with a frequency above 30 MHz use _______propagation.
Ground
Sky
Line-of-sight
None of the above
Ans – (3)
Explanation –
Line-of-Sight Propagation – At frequencies above 30 MHz (typically in the VHF, UHF, and microwave bands), radio waves propagate in a straight line between the transmitting and receiving antennas.
This requires an unobstructed line-of-sight path between the antennas, meaning there should be no significant obstacles such as hills, buildings, or other obstructions blocking the direct path.
Q187 – _______ cable is used for voice and data communications.
Coaxial
Fiber-optic
Twisted-pair
None of the above
Ans – (3)
Explanation – Twisted-pair cable is commonly used for voice and data communications.
Twisted-pair Cable – This type of cable consists of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together. It is widely used in telecommunications for telephone lines (voice communication) and in Ethernet networks (data communication). The twisting of the wires helps to reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk between pairs of wires, improving the overall performance of the cable.
Q188 – Radio waves are _________.
Omnidirectional
Unidirectional
Bidirectional
None of the above
Ans – (1)
Explanation –
Omnidirectional – This means that radio waves can propagate in all directions from the source. They can spread out uniformly in every direction, making them suitable for broadcasting and mobile communications where the signal needs to reach multiple receivers in different locations.
Q189 – The meaning of Straight-through Cable is
Four wire pairs connect to the same pin on each end
The cable Which Directly connects Computer to Computer
Four wire pairs not twisted with each other
The cable which is not twisted
Ans – (1)
Explanation – The meaning of a straight-through cable is ‘Four wire pairs connect to the same pin on each end’.
Straight-through Cable – This type of cable is commonly used in networking to connect different types of devices, such as a computer to a switch or a router to a hub. In a straight-through cable, each wire in the cable is connected to the same pin number on both ends. For example, pin 1 on one end connects to pin 1 on the other end, pin 2 connects to pin 2, and so on.
Computer to Computer Connection – For connecting two computers directly without any intermediary network devices, a crossover cable is typically used, not a straight-through cable.
Wire Pair Twisting – The twisting of wire pairs helps to reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk. In a straight-through cable, the wire pairs are twisted, just like in other Ethernet cables, to maintain signal integrity.
Q190 – The amount of data that can be carried from one point to another in a given time period is called
Scope
Capacity
Bandwidth
Limitation
Ans – (3)
Explanation – The amount of data that can be carried from one point to another in a given time period is called Bandwidth.
This term refers to the maximum rate at which data can be transmitted over a network or communication channel.
It is typically measured in bits per second (bps) or its multiples, such as kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps).
Higher bandwidth indicates a higher capacity for data transfer, meaning more data can be transmitted in a given time period.
Scope – This term generally refers to the extent or range of something, not specifically to data transfer rates.
Capacity – While related to bandwidth, capacity can refer more broadly to the total amount of data that a system can handle or store, not necessarily the rate of data transfer.
Limitation – This term refers to restrictions or constraints, not specifically to the rate of data transfer.
Q191 – In 10base2, 10base5, what does 2 and 5 stand for?
Speed in mbps
Number of segments
Length of segment
Size of segment
Ans – (3)
Explanation –
In 10base2 and 10base5, the numbers 2 and 5 stand for the maximum length of segment in hundreds of meters.
Q192 – Data from a computer are _______; the local loop handles _______ signals.
analog; analog
analog; digital
digital; digital
digital; analog
Ans – (4)
Explanation –
The local loop refers to the physical link between the customer’s premises and the telecommunications provider’s central office.
Traditionally, this link handles analog signals, particularly in the case of standard telephone lines (POTS – Plain Old Telephone Service). Even when digital data from a computer needs to be transmitted over these lines, it is often converted to analog form using a modem for compatibility with the analog local loop infrastructure.
Q193 – _______ is suitable for businesses that require comparable upstream and downstream data rates.
VDSL
ADSL
SDSL
Both (a) and (b)
Ans – (3)
Explanation –
SDSL (Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line) is suitable for businesses that require comparable upstream and downstream data rates.
This technology provides equal bandwidth for both upstream and downstream data rates, making it ideal for businesses that need to send and receive large amounts of data equally.
VDSL (Very-high-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line) – VDSL can offer high speeds for both upstream and downstream data rates, but the rates are not necessarily symmetric. It is more common for VDSL to have higher downstream speeds compared to upstream speeds.
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) – ADSL provides higher download speeds compared to upload speeds, making it suitable for typical consumer use where downloading data is more frequent than uploading.
Q194 – The largest portion of the bandwidth for ADSL carries _______.
Voice communication
Upstream data
Downstream data
Control data
Ans – (3)
Explanation –
ADSL is designed to provide higher data rates for downloading (downstream) than for uploading (upstream). This asymmetry is based on the typical usage patterns of most internet users, who generally download more data (e.g., streaming videos, browsing the web) than they upload (e.g., sending emails, uploading files).
Q195 – In an HFC network, the downstream data are modulated using the _______ modulation technique.
PSK
QAM
PCM
ASK
Ans – (2)
Explanation – In an HFC (Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial) network, the downstream data are modulated using the QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) technique.
QAM is widely used in HFC networks for modulating downstream data. It combines both amplitude modulation and phase modulation to increase the number of bits per symbol, making it highly efficient for transmitting large amounts of data over the network.
Q196 – The modern telephone network is now ________.
Digital
Analog
Digital as well as analog
None of the above
Ans – (3)
Q197 – The original telephone network, which is referred to as the plain old telephone system (POTS), was an ________ system.
Digital
Analog
Digital as well as analog
None of the above
Ans – (2)
Explanation – POTS was originally designed to carry analog voice signals.
In an analog system, the voice signals are represented by continuous waves, which are directly transmitted over the network.
Q198 – The protocol that is used for signaling in the telephone network is called ______.
POP
SSS
SS7
None of the above
Ans – (3)
Explanation – The protocol that is used for signaling in the telephone network is called SS7 (Signaling System 7).
SS7 is a set of signaling protocols used in telecommunications networks to control the setup, management, and teardown of telephone calls. It is used for functions such as call setup, routing, billing, and network management.
SS7 enables seamless communication between different telecommunications service providers and is crucial for the operation of modern telephone networks.
Q199 – Telephone companies provide two types of analog services: analog _______ services and analog _____services.
Switched; in-band
Out-of-band; in-band
Switched; leased
Leased; out-of-band
Ans – (3)
Explanation –
Analog Switched Services – These are traditional telephone services where calls are switched dynamically between different users based on their dialing patterns. This includes services like basic voice calls and dial-up internet connections.
Analog Leased Services – These are dedicated analog circuits leased to customers for exclusive use over a specific period. They are typically used for point-to-point data connections, such as leased lines for private branch exchanges (PBXs), video conferencing, or dedicated internet access.
Q200 – What is the max cable length of STP?
100 ft
200 ft
100 m
200 m
Ans – (3)
Explanation –
The maximum cable length of STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) is 100 meters.
STP cables are commonly used in Ethernet networks. The maximum recommended length for STP cables is typically 100 meters (about 328 feet). This length limitation helps to maintain signal integrity and performance within the network.
UTP cables, which are more common than STP cables, also have a maximum length of 100 meters for Ethernet networks.



