Unit 1
Father of Algorithm, What is Algorithm, Need of an algorithm, Algorithm Vs Program, Good Algorithm, Analysis of Algorithm, Comparison of running time, Asymptotic notation, Recurrence relation, Substitution method, Iterative method, Recurrence Tree Method, Master Theorem, Extended Master Theorem.
Q61 – Find the time complexity
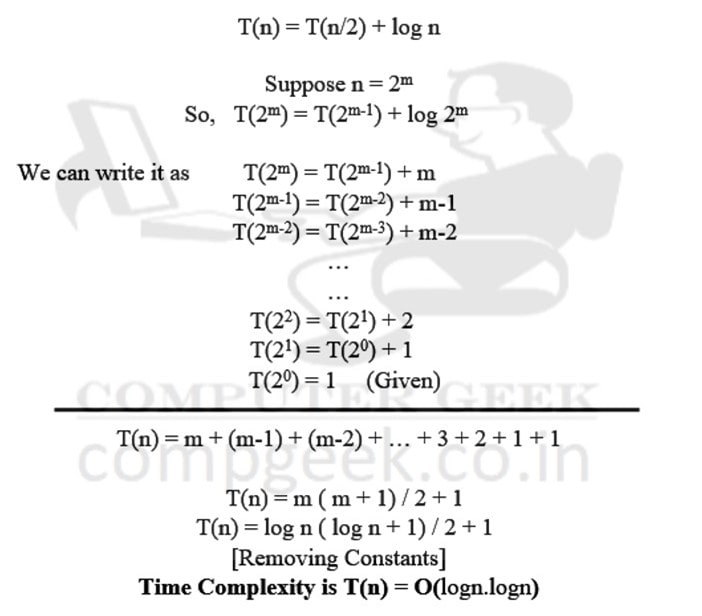
T(n) = T(n/2) + logn
T(1) = 1
O(logn)
O(logn.logn)
O(nlog2 n)
O(nlogn)
Ans – (2)
Explanation –
Q62 – Find the time complexity
T(n) = T(n/2) + nlogn
T(1) = 1
O(logn)
O(log2n)
O(nlog2n)
O(nlogn)
Ans – (4)
Explanation –

Q63 – Find the time complexity
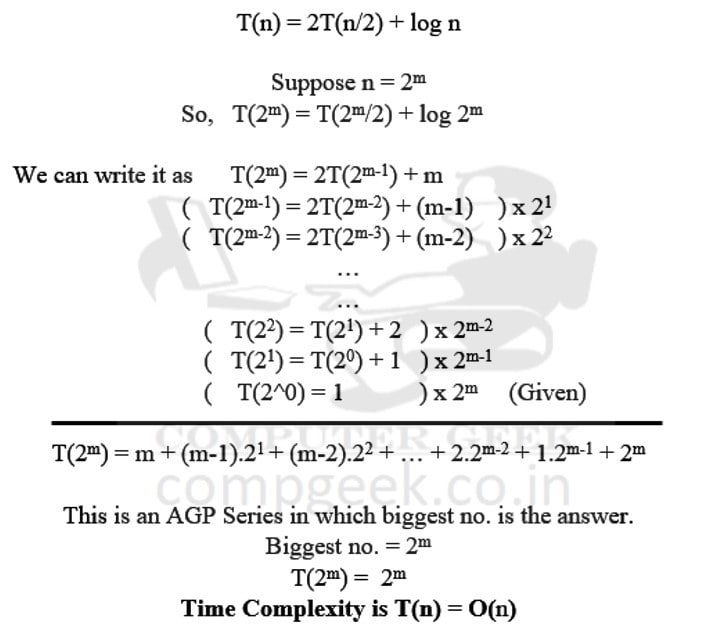
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + logn
T(1) = 1
O(n)
O(logn)
O(nlogn)
O(n2logn)
Ans – (1)
Explanation –
Q64 – Find the time complexity
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + nlogn
T(1) = 1
O(n)
O(log2n)
O(nlognlogn)
O(nloglogn)
Ans – (3)
Explanation –

Q65 – Find the time complexity
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + n/logn
T(1) = 1
O(n)
O(nlogn)
O(nlognlogn)
O(nloglogn)
Ans – (4)
Explanation –

Q66 – Find the time complexity
T(n) = T(√n) + 1
T(2) = 1
O(n)
O(nlogn)
O(lognlogn)
O(loglogn)
Ans – (4)
Explanation –

Q7 – Find the time complexity
T(n) = T(√n) + logn
T(2) = 1
O(n)
O(logn)
O(lognlogn)
O(loglogn)
Ans – (2)
Explanation –

Q68 – Find the time complexity
T(n) = 2T(√n) + 1
T(1) = 1
O(n)
O(logn)
O(lognlogn)
O(loglogn)
Ans – (2)
Explanation –

Q69 – Find the time complexity
T(n) = 2T(√n) + logn
T(1) = 1
O(logn.logn)
O(logn)
O(logn.loglogn)
O(nloglogn)
Ans – (3)
Explanation –

Q70 – Find the time complexity
T(n) = 5T(√n) + logn
T(1) = 1
O(n.(logn)log25)
O((logn)log25)
O(nlog5n)
O(logn.log5n)
Ans – (2)
Explanation –

Q71 – Arrange the given items in ascending order for large n.
The terms are n2, nlogn, n, 2n, 2logn, 4logn, 3n.
1. n, nlogn, n2, 2logn, 4logn, 2n, 3n
- n, nlogn, 2logn, 4logn, n2, 2n, 3n
- n, 2logn, 4logn, nlogn, n2, 2n, 3n
- n, 2logn, nlogn, n2, 4logn, 2n, 3n
Ans – (4)
Explanation –

Q72 – Find the time complexity
T(n) = √nT(√n) + n
T(1) = 1
O(n.logn)
O(n.loglogn)
O(logn)
O((logn)2)
Ans – (2)
Explanation –

Q73 – Arrange the given items in ascending order for large n.
The terms are n2, nlogn, n, 2n, 2logn, 4logn, 3n
n, nlogn, n2, 2logn, 4logn, 2n, 3n
n, nlogn, 2logn, 4logn, n2, 2n, 3n
n, 2logn, 4logn, nlogn, n2, 2n, 3n
n, 2logn, nlogn, n2, 4logn, 2n, 3n
Ans – (4)
Explanation – Let’s say n = 64
Then, n = 64
- 2logn = 26 = 64
- nlogn = 64*6 = 384
- n2 = 642 = 4096
- 4logn = 4log64 = (22)6 = (26)2 = 642 = 4096
- 2n = 264
- 3n = 364
Q74 – Arrange given terms in ascending order for large n.
The terms are √logn, (loglogn)2, logn*loglogn, logn/loglogn, √logn/loglogn.
√logn/loglogn, √logn, logn/loglogn, (loglogn)2, logn*loglogn
√logn/loglogn, √logn, logn/loglogn, logn*loglogn, (loglogn)2
(loglogn)2, √logn/loglogn, √logn, logn/loglogn, logn*loglogn
(loglogn)2, √logn/loglogn, logn/loglogn, √logn, logn*loglogn
Ans – (3)
Explanation – Let’s say n = 22^128
Then,
- (loglogn)2 = (loglog 22^128)2 = 1282 = (27)2 = 214
- √logn/loglogn = √log 22^128 / loglog 22^128 = 264/27 = 257
- √logn = √log 22^128 = 264
- logn/loglogn = log 22^128/loglog 22^128 = 2128/27 = 2121
- logn*loglogn = log 22^128*loglog 22^128 = 2128*128 = 2128*27 = 2135
Q75 – Arrange given terms in ascending order for large n.
The terms are √nlogn , (logn)logn, (loglogn)n, (logn)√n , nloglogn, n2.
nloglogn = (logn)logn < √nlogn < (logn)√n < (loglogn)n < n2
n2 < nloglogn = (logn)logn < √nlogn < (logn)√n < (loglogn)n
n2 < nloglogn < (logn)logn = (logn)√n < (loglogn)n < √nlogn
√nlogn < n2 < nloglogn < (logn)logn = (logn)√n < (loglogn)n
Ans – (2)
Explanation – Taking logarithm of the terms and n = 22^8
log(√nlogn) = Logn*log√n = 28*(1/2)*28 = 215
Log(logn)logn = Logn*loglogn = 28*8 = 28*23 = 211
Log(loglogn)n = n*log(loglogn) = 22^8*3 = 2256*3 ≈ 2257
Log(logn)√n = √n*loglogn = 22^4*8 = 216*23 = 219
Log(nloglogn) = Loglogn*logn = 8*28 = 23*28 = 211
Log(n2) = 2logn = 2*28 = 29
Then, n2 < nloglogn = (logn)logn < √nlogn < (logn)√n < (loglogn)n
Q76 – Arrange given terms in ascending order for large n.
The terms are 1, 2, n1/n, n1/logn, (logn)1/logn
1, n1/n, n1/logn, (logn)1/logn, 2
(logn)1/logn, 1, n1/n, 2, n1/logn
1, n1/n, (logn)1/logn, 2, n1/logn
1, (logn)1/logn, 2, n1/logn, n1/n
Ans – (3)
Explanation – Taking logarithm of the terms and n = 216
Log 1 = 0
Log 2 = 1
Log(n)1/n = 1/n*logn = (1/216)*16 = 24/216 = 2-12
Log(n1/logn) = (1/logn)*n = (1/16)*216 = 216/24 = 212
Log(logn)1/logn = 1/logn*loglogn = (1/16)*4 = 2-2
Then, 1 < n1/n < (logn)1/logn < 2 < n1/logn.
Q77 – Arrange given terms in ascending order for large n.
The terms are √logn, (loglogn)n, (logn)1/logn, 1/logn, (logn)√n.
1/logn, (logn)1/logn, √logn, (loglogn)n, (logn)√n
1/logn, (logn)1/logn, (logn)√n, √logn, (loglogn)n
(logn)1/logn, 1/logn, √logn, (logn)√n, (loglogn)n
1/logn, (logn)1/logn, √logn, (logn)√n, (loglogn)n
Ans – (4)
Explanation – Let’s say n = 216
√logn = √log216 = √16 = 4
(loglogn)n = (loglog216)2^16 = (log 16)2^16 = 42^16 = 465536
(logn)1/logn = (log 216)1/log2^16 = 161/16 = 1.18
1/logn = 1/log 216 = 1/16 = 0.0625
(logn)√n = (log 216)√(2)^16 = 162^8 = 4512
The answer is 1/logn, (logn)1/logn, √logn, (logn)√n, (loglogn)n.
Q78 – Find the time complexity by recurrence relation
T(n) = T(n/2) + T(n/4) + T(n/8) + n
O(logn)
O(nlogn)
O(n2)
O(loglogn)
Ans – (2)
Explanation –
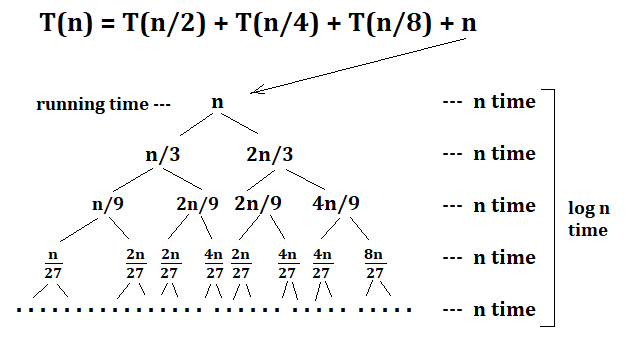
After summation all the operations = n + n + n + … + n [log n time ]
= n.logn
= O(n.logn) is the Answer
Q79 – Find the time complexity by recurrence relation
T(n) = T(n/3) + T(2n/3) + n
O(logn)
O(nlogn)
O(n2)
O(loglogn)
Ans – (2)
Explanation –
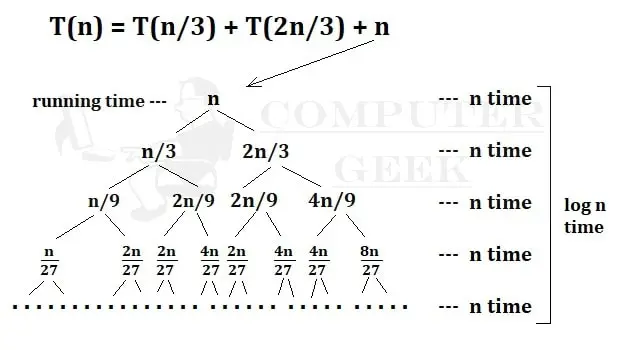
After summation all the operations = n + n + n + … + n [log n time ]
= n.logn
= O(n.logn) is the Answer
Q80 – Solve the time complexity by recurrence tree method?
T(n) = T(n-1) + T(n-2) + 1
T(0) = 0, T(1) = 1
O(n2)
O(n!)
O(n2logn)
O(2n)
Ans – (4)
Explanation – By recurrence tree method, we get
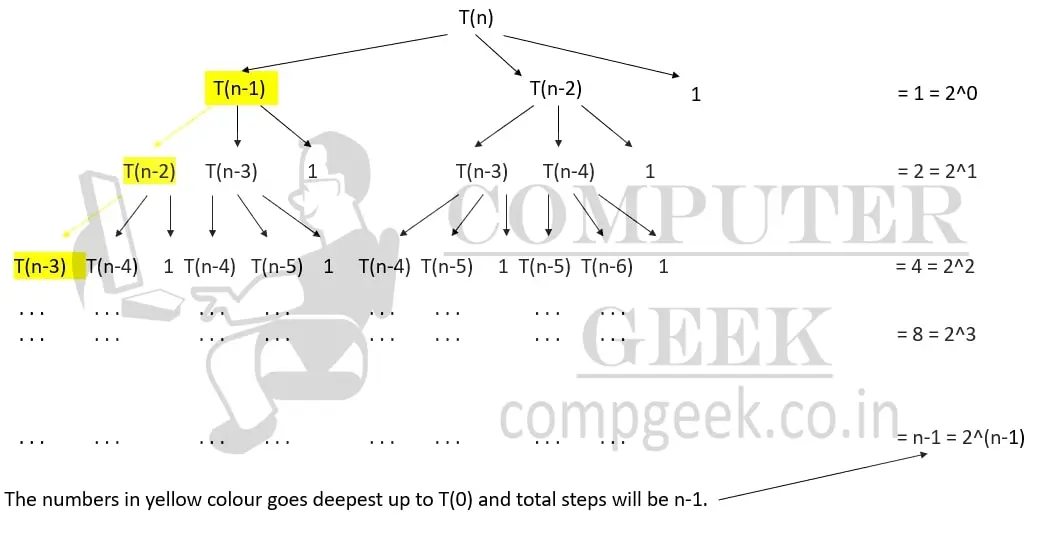
The running time we get when T(n) is broken is 20. When further broken down we get 21, 22, 23, …, 2n-1.
Sum = 20 + 21 + 22 + 23 + …+ 2n-1
This is a G.P. Series and sum = a(rn – 1)/(r-1) where r = 2
=> 20(2n-1 – 1)/(2-1)
=> 2n
The time complexity of the recurrence T(n) = T(n-1) + T(n-2) + 1 is O(2n).






